Research Topics
Research Topics
Our research efforts are concentrated in the field of concrete engineering, focusing on innnovative construction technnology and materials for sustainable society development.
本研究室では、次世代の建設技術や持続可能な社会構築に向けた建設材料の評価に関する研究を行っています。
-
- 3D concrete printing and material/structural evaluation Click!
3Dコンクリートプリンティング技術と材料および力学性能評価
- 3D concrete printing and material/structural evaluation Click!
- Immbilization and transportation of radioactive nuclides with cementitious materials Click!
セメント系材料中の放射性核種の閉じ込め性能および移行挙動 - Non-destructive techniques for interior structure of concrete based with pulsed laser irradiation Click!
パルスレーザー照射によるセメント硬化体を対象とした非破壊検査手法の構築 - Application of synchrotron X-ray to evluation of hydrated cement systems Click!
X線を用いたセメント材料中の空隙および水和生成相の同定による内部構造と物質移行性 - CO2 absorption and quality assessment method of recycled aggregate for concrete Click!
CO2固定化による再生骨材改質と品質評価手法の開発 - Application of AI analysis on monitoring and diagnosis information of concrete infrastructures Click!
コンクリート構造物を対象としたモニタリングデータに基づく点検および診断の情報解析とAI技術の活用 - Visualization of crack in concrete by means of ultrasonic vibration and infrared thermal imaging Click!
超音波による超高サイクル応力付与と赤外線サーモグラフィを併用したコンクリートの物性評価 - Development of sensing device with MEMS technology for structural and environmental condition in service Click!
インフラモニタリングおよび環境センシングを目的とした革新的MEMS技術によるデバイス開発 - Utilization of industrial by-products as cementitious materials and corrosion resistance of reinforced concrete Click!
産業副産物の積極的利用と鉄筋コンクリートの耐久性
3D concrete printing and material/structural evaluation
3Dコンクリートプリンティング技術と材料および力学性能評価
3Dプリンティング技術によりコンクリート構造物を造形するとき,使用材料の選定および配合に加えて,造形条件(積層パラメータ)を適切に設定することが重要です。従来の流込み施工では,同材料および同配合を使用したコンクリートは同様の性能を有する一方で,3Dプリンティング施工では,同材料および同配合を使用しても,異なる積層パラメータにより造形したとき,造形されたコンクリートの性能は大きく異なります。これを利用して本研究では,使用材料,配合および積層パラメータによって,3Dプリンティングにより造形したコンクリートの性能を制御および予測することを目的としています。
When constructing 3D printed concrete, it is important to set the appropriate fabrication conditions (printing parameters), in addition to designing the materials and mix proportions. Conventional cast concrete has similar performance when using the same materials and mix proportions. In contrast, 3D printed concrete has a different performance with different printing parameters, even when using the same materials and mix proportions. This study aims to control and predict the performance of 3D printed concrete based on materials, mix proportion and printing parameters.
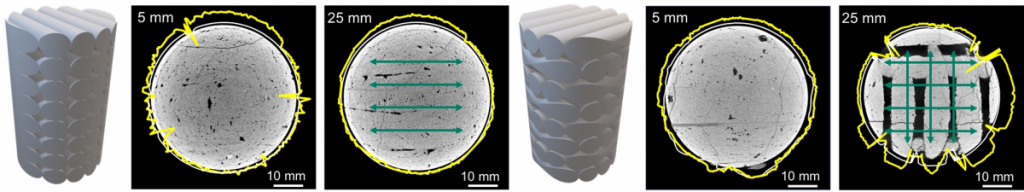
Three-dimensional deformation of 3D printed concrete.
Strain distribution of 3D printed concrete detected by digital image correlation.
研究業績の一例
Nakase, K. Hashimoto, T. Sugiyama, K. Kono, Evaluation of Internal Cracks and Three-Dimensional Deformation due to Different Nozzle Paths in a Material Extrusion 3D Printer
Proceedings of the 16th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement 2023 (ICCC2023), pp.13-17, 2023.
その他の研究成果
中瀬皓太,橋本勝文,杉山隆文,河野克哉,建設用3Dプリンタの積層経路が異なるモルタル積層体の圧縮破壊時におけるひび割れ進展挙動と変形分布の関係
コンクリート工学年次論文集,Vol.45,No.1,pp.1600-1605, 2023.
Immbilization and transportation of radioactive nuclides with cementitious materials
セメント系材料中の放射性核種の閉じ込め性能および移行挙動
放射性廃棄物の合理的処分には,コンクリート内部での放射性核種の拡散性評価が重要です。放射性コンクリート廃棄物を模擬し,核種イオンの移行挙動を評価するための研究を行っています。特に,X線CT画像,LIBSやEPMAによる元素分析を用いた核種の移行挙動評価の妥当性を評価しています。また,セメント水和物の相組成に着目したイオン移動に伴う変質を再現するSiTram(同時イオン輸送モデル)を開発しています。イオン移動とカルシウム水和物の溶解を連成したアルゴリズムにより,実際の環境暴露をシミュレートするさまざまな境界条件やひび割れの影響を明らかする検討を行っています。
An original computer simulation program, SiTram (Simultaneous Ions Transport Model), was developed and is continually updated for the precise calculation of ionic diffusion and alteration of hydrated cement systems. Unique features of this simulation program include the coupled calculation of the diffusion of chloride and calcium dissolution. Furthermore, the effect of cracks on the transport phenomenon in concrete is clarified considering different boundary conditions that simulate real environmental exposure.
研究業績の一例
Yingyao Tan, Takafumi Sugiyama and Kastufumi Hashimoto, Evaluation of transport properties of deteriorated concrete due to calcium leaching with coupled CT image analysis and random walk simulation
Construction and Building Materials, Vol.369, 130526, 2023.
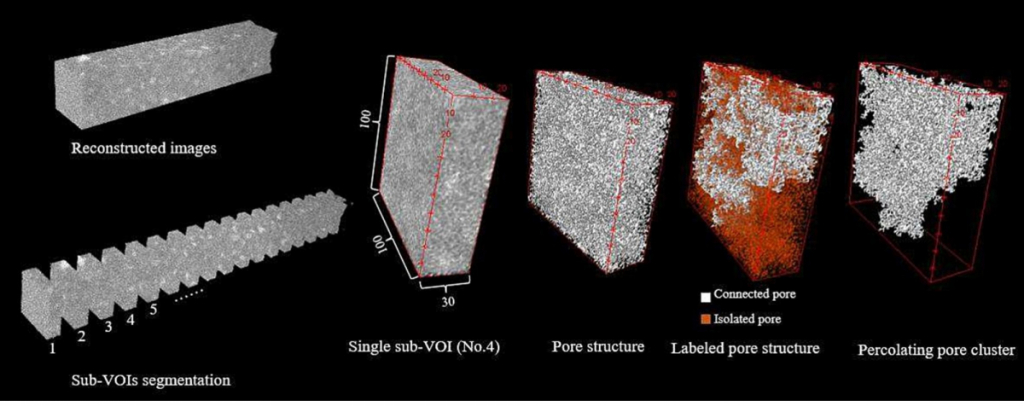
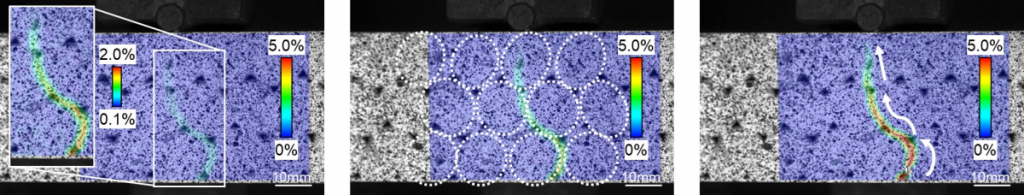
Demonstration of extracting pore structure from 3D geometry of X-ray image.
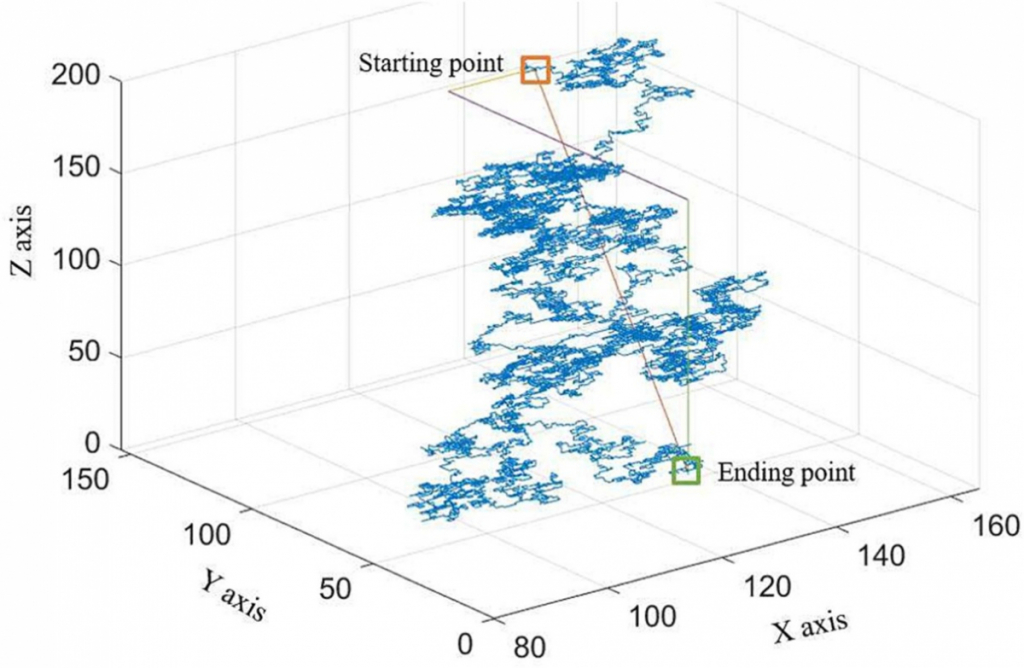
Random walk simulation in X-ray CT image analysis.
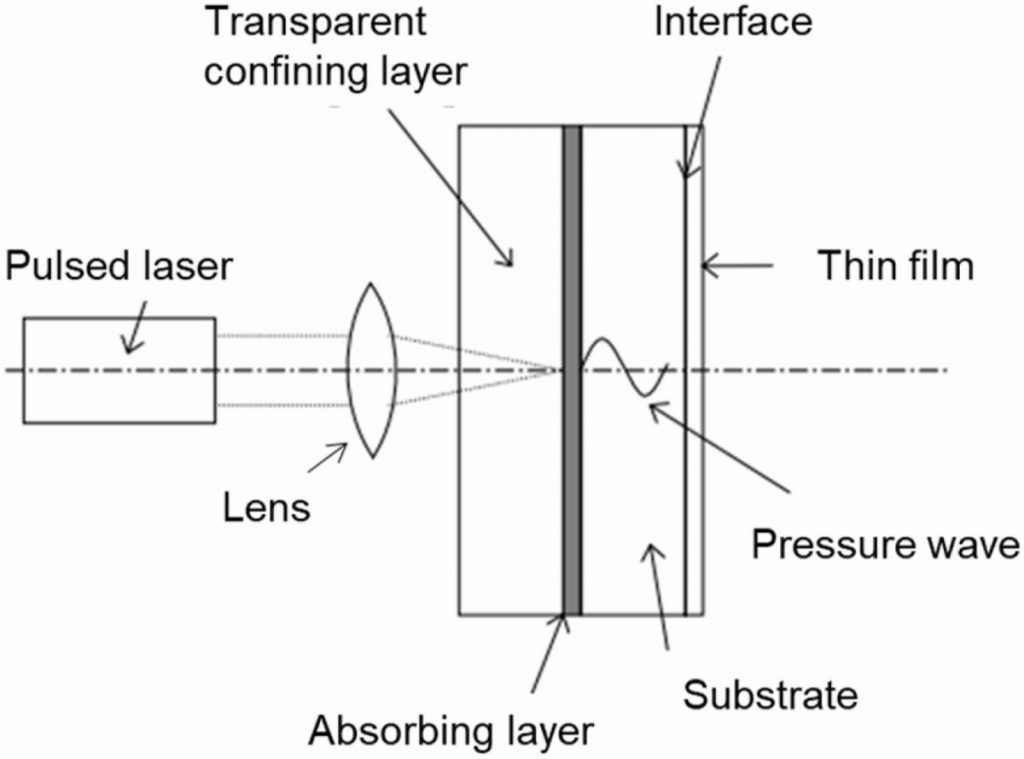
Non-destructive techniques for interior structure of concrete based with pulsed laser irradiation
パルスレーザー照射によるセメント硬化体を対象とした非破壊検査手法の構築
コンクリート内部のひび割れ等の損傷および欠陥検出や部材厚の測定には,超音波帯域の弾性波を用いた非破壊検査手法(超音波法)が広く適用されています。しかしながら,センサ設置等の作業に近接する必要があり,検査の簡便性や迅速性に課題が残されたままとなっているのが現状です。超音波法の高度(高速・非接触(遠隔))化を目的として,レーザー照射による弾性波励起手法を構築することで,コンクリート工学分野と光量子科学分野を横断した学術的アプローチを検討しています。固体物性理論と熱弾性理論の異なる物理現象による弾性波の励起特性から,超音波帯域の弾性波励起を目的としたレーザー照射条件と非接触超音波法の実践的な適用範囲を明確することを目的としています。
Nondestructive inspection methods (ultrasonic methods) using elastic waves in the ultrasonic range are widely applied to detect damage and defects such as cracks in concrete and to measure the thickness of structural members. In order to develop an advanced (high-speed, non-contact (remote)) ultrasonic method, we are investigating the excitation characteristics of elastic waves by different physical phenomena of solid state physics theory and thermoelasticity theory. It is aimed to clarify the suitable laser irradiation conditions in purposes of the elastic wave excitation in the ultrasonic band.
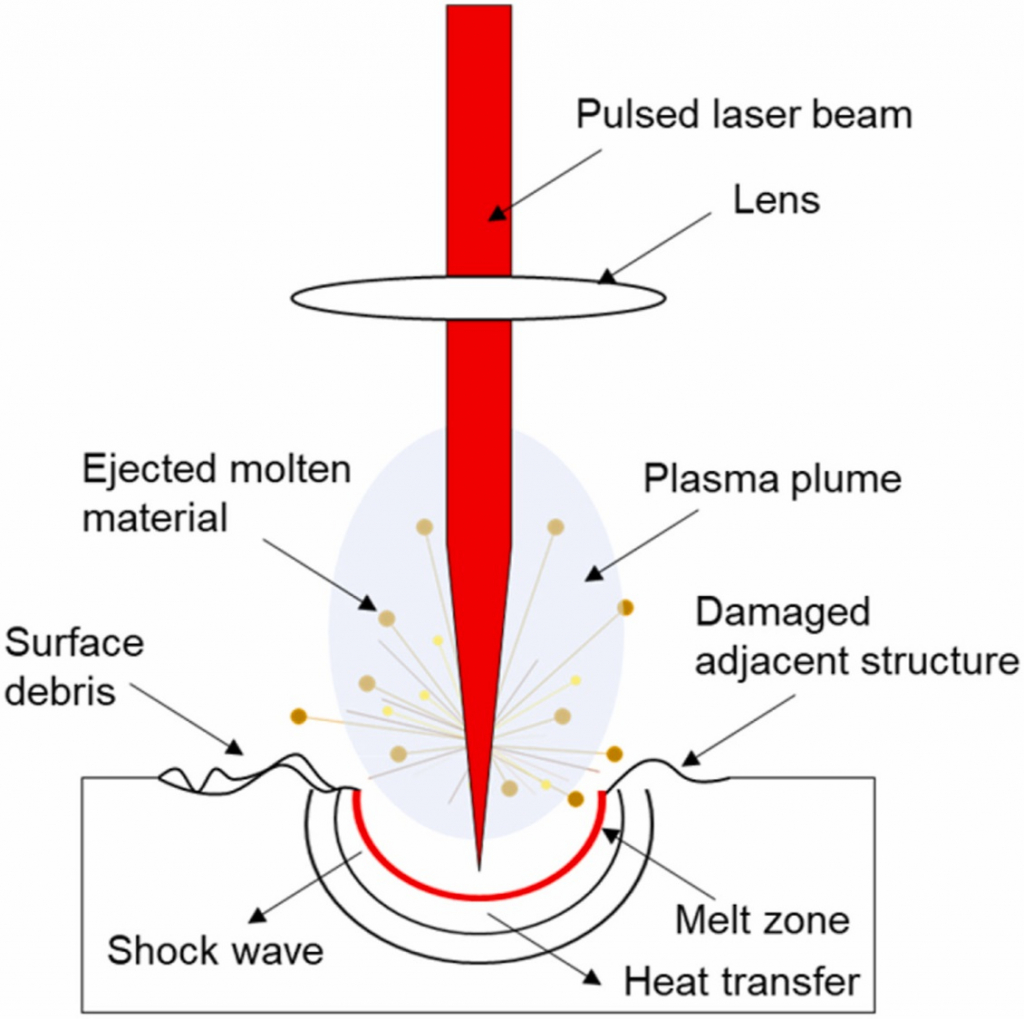
Laser ablation principle.
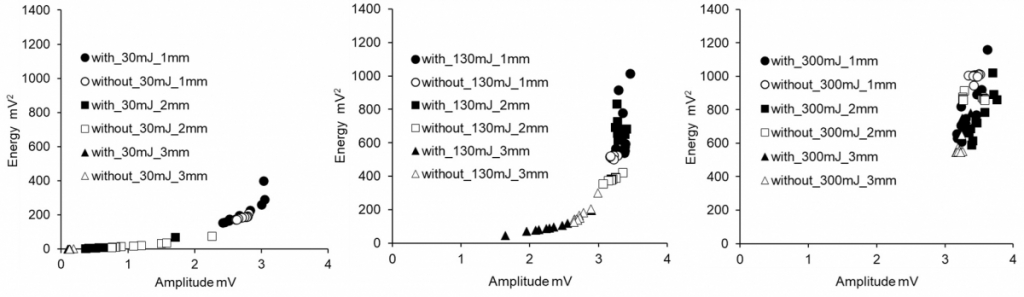
Amplitude and energy of detected AE signals due to laser irradiation on cement paste surface.
研究業績の一例
Katsufumi Hashimoto and Tomoki Shiotani, Induction and Amplification of Elastic Wave into Cementitious Material by Applied Laser Ablation System
Developments in the Built Environment, Vol.12, 100099, 2022.
その他の研究成果
Katsufumi Hashimoto, Tomoki Shiotani, Masayasu Ohtsu, Application of Impact-Echo Method to 3D SIBIE Procedure for Damage Detection in Concrete
Applied Sciences, 10(8), 2729, 2020.
Application of synchrotron X-ray to evluation of hydrated cement systems
放射線技術を核としたコンクリートの効率的な物理化学組成の評価技術の構築
兵庫県にある大型放射光施設SPring-8の放射光X線を用いて,セメント水和物の相組成や硬化体内部の空隙構造に関する材料特性を解明する研究を行っています。CT-XRD連成法により,損傷・劣化したセメント系材料の物理的・化学的変化を調べるために,マイクロフォーカスX線CT(コンピュータ断層撮影)システムを用いて、コンクリートの微細構造を可視化する技術を開発しています。物理化学的なナノ~マイクロレベルのコンクリート中の微小領域における空隙径,屈曲度,連続性を定量化することができます。
The characteristics of hydrated cement systems are clarified using synchrotron X-ray at the SPring-8 facility in Hyogo Prefecture, Japan. A non-destructive integrated CT-XRD method has been developed and applied to study the physical and chemical changes in damaged and deteriorated cementitious materials. Using an industrial microfocus X-ray CT (Computed Tomography) system, concrete microstructure can be visualized. From this visualization, the pore structure can be quantified over time by means such as effective porosity, diffusion tortuosity, and the degree of connectivity.
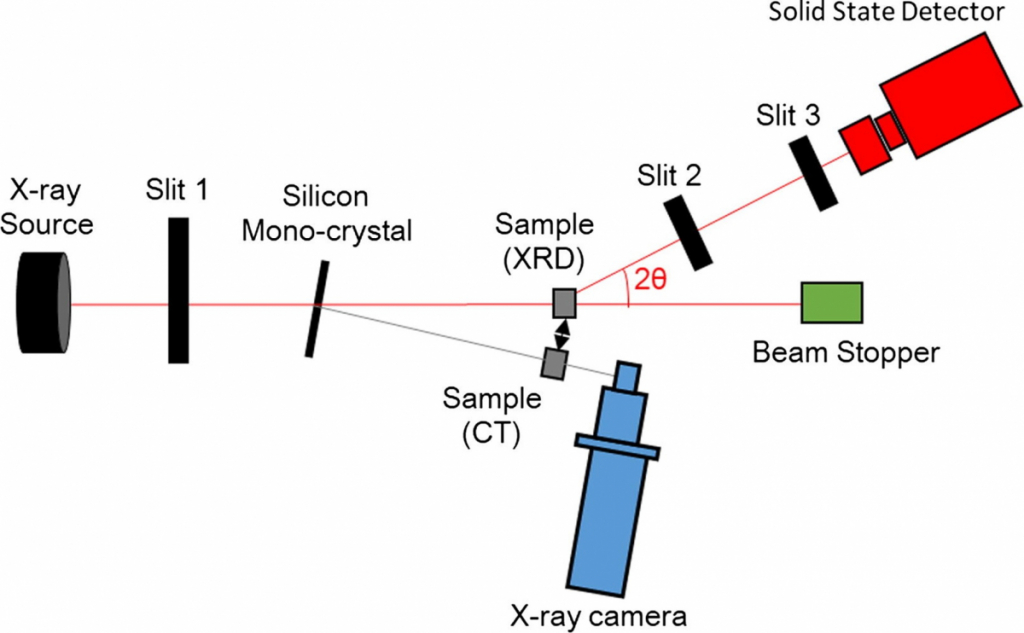
Schematic diagram of the system for non-destructive integrated CT-XRD method.
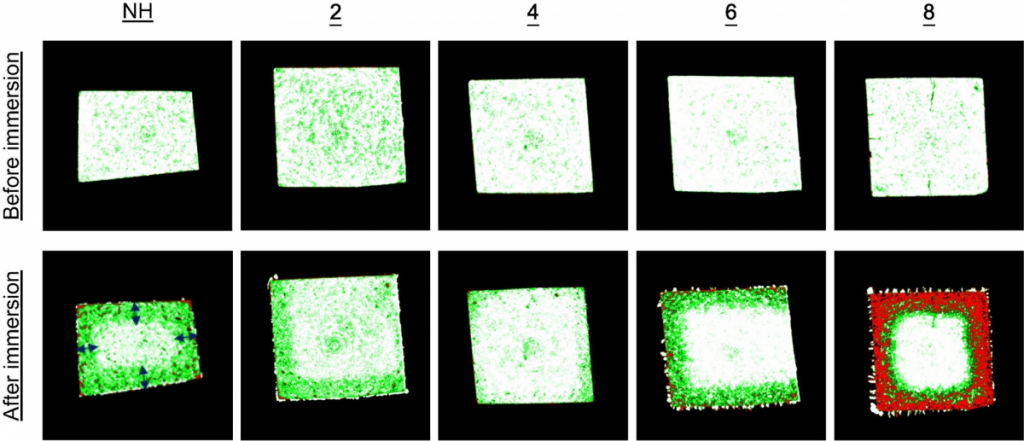
Region of Interest extracted from original data set and visualization of leaching area from phase segmentation.
研究業績の一例
H. Takahashi and T. Sugiyama, Application of non-destructive integrated CT-XRD method to investigate alteration of cementitious materials subjected to high temperature and pure water
Construction and Building Materials, 203, pp.579-588, 2019.
その他の研究成果
Takafumi Sugiyama and Michael Angelo B. Promentilla, Advancing Concrete Durability Research through X-ray Computed Tomography
Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 19(6), pp.730-755, 2021.
CO2 absorption and quality assessment method of recycled aggregate for concrete
CO2固定化による再生骨材改質と品質評価手法の開発
品質評価手法を再生骨材の改質および製造工程に組み込むことで,CO2固定化による品質改善効果と必要なエネルギーおよびコストを最適化できると考えています。本研究では,炭酸化前後の再生骨材の品質分類にレーザー加振法を適用することで,CO2固定化と品質改善の評価・検査技術を構築します。提案する手法をCO2固定化による品質評価プロセスと炭酸化再生骨材の製造工程へ導入することで,再生骨材の炭酸化による品質改善と製造工程の最適化により,当該観点からコンクリートのカーボンニュートラル社会への貢献を最大化できるのではないかと考えています。
It is strongly believed that incorporating quality assessment methods into the modification and manufacturing process of recycled aggregate will optimize the quality improvement effect of CO2 capture as well as the energy and cost requirements. In this study, irradiated laser vibration method is applied to quality classification of recycled aggregate before and after carbonation to establish an evaluation and inspection technique for carbon capture and quality improvement. By introducing the proposed method into the quality evaluation process by CO2 capture and the manufacturing process of carbonated recycled aggregate, the quality improvement by carbonation of recycled aggregate and the optimization of the manufacturing process will maximize the contribution of concrete to a carbon neutral society.
Laser ablation and spallation technique.
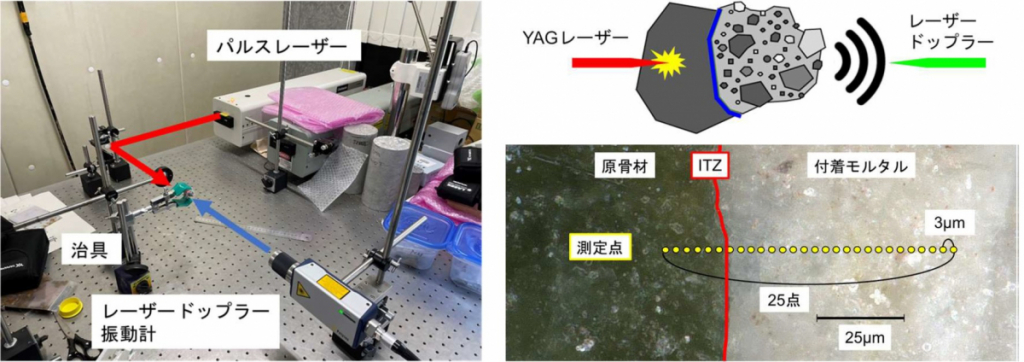
Overview of laser vibration method for quality assessment of recycled aggregate.
研究業績の一例
橋本勝文、塩谷智基、AEセンサを用いたレ-ザ-励起弾性波のコンクリ-ト中の伝搬評価
超音波テクノ,Vol.32,No.3,pp.29-32,2020.
その他の研究成果
村瀬春祐、橋本勝文、塩谷智基、河野広隆、服部篤史、レ-ザ-照射表面の状態がコンクリ-ト中への励起弾性波に及ぼす影響
コンクリ-ト構造物の補修,補強,アップグレ-ド論文報告集,Vol.20,pp.373-376,2020.
Application of AI analysis on monitoring and diagnosis information of concrete infrastructures
コンクリート構造物を対象としたモニタリングデータに基づく点検および診断の情報解析とAI技術の活用
社会基盤施設を構成するコンクリート構造物が老朽化し,膨大な点検および調査による診断業務が増加することが懸念される一方で,目視点検や打音検査を実施する熟練した技術を要する点検者の不足が問題となっています。本研究では,経験に基づく専門的かつ高度な知識がなくても簡単かつ効率的にコンクリート構造物の状態や劣化に対する検査を行うことのできるAIツールの構築を目指しています。特に,画像や打音波形の深層学習を自動で行うことが出来るアプリケーションやソフトウェアのクラウドシステム開発を行っています。
Concrete structures for social infrastructure are aging through their long service life, and there is serious concern about an increase in diagnosis operation due to the vast amount of inspections and investigations. In this research, it is aimed to construct AI tools that can easily and efficiently inspect the condition and deterioration of concrete structures without specialized and advanced knowledge based on experience. In particular, we are developing a cloud system of applications and software that can automatically perform deep learning of images and waveforms obtained from respective inspection techniques.
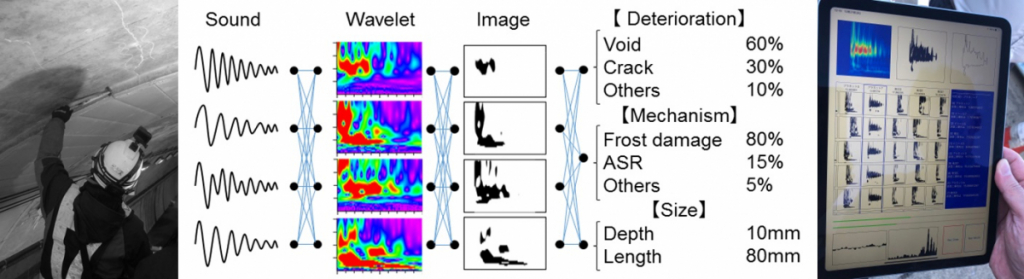
Wavelet analysis for acoustic sound detected by tapping concrete surface.
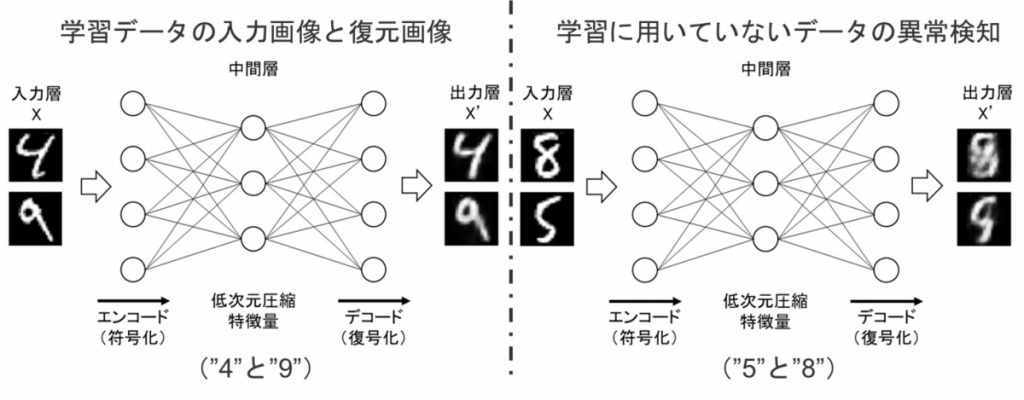
Outline of autoencoder for unsupervised learning for data anomaly detection.
研究業績の一例
Katsufumi Hashimoto, Tomoki Shiotani, Takahiro Nishida, Hideo Kumagai, Katsuhiko Kokubo, Development of Autonomous Hammering Test Method for Deteriorated Concrete Structures based on Artificial Intelligence and 3D Positioning System
Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering, pp.219-228, 2019.
その他の研究成果
Hisafumi Asaue, Tomoki Shiotani, Takahiro Nishida, Katsufumi Hashimoto, Two-Dimensional Source Location of Acoustic Emission by Means of AI
Springer Proceedings in Physics, No.218, pp.131-138, 2019.
Visualization of crack in concrete by means of ultrasonic vibration and infrared thermal imaging
超音波による超高サイクル応力付与と赤外線サーモグラフィを併用したコンクリートの物性評価
Sonic-IR法(サーモソニック法)は超音波による材料の発熱現象に着目した赤外線を用いたイメージング手法です。モルタルやコンクリートなどのセメント系材料の破壊領域やひび割れ進展領域の検出に利用できると考えています。また,圧縮応力を受けるモルタルの損傷程度に伴う破壊の進行や、コンクリート中の模擬ひび割れ部における補修状態を定量的に明らかにすることが可能であることを実験的かつ解析的に解明することを検討しています。さらに,超音波領域の繰返し周波数において圧縮応力を付与可能とする試験条件において,超音波セメント系材料の特性評価に適したメカニズムの妥当性を検証することを目的とした研究を行っています。
Sonic-IR imaging technique can be utilized for detecting the fracture area and the crack propagation zone in cementitious materials such as mortar and concrete, although it is known that the technique is usually introduced for metals or composite materials which have high thermal conductivity. It is also enabled to quantitatively clarify the fracture progress with damage degree of mortar subjected to the compression stress and the repaied condition at the simulated crack in concrete. In this study, the ultrasonic excitation method is introduced in order to investigate the validity of the suitable mechanism for evaluation of cementitious material property.
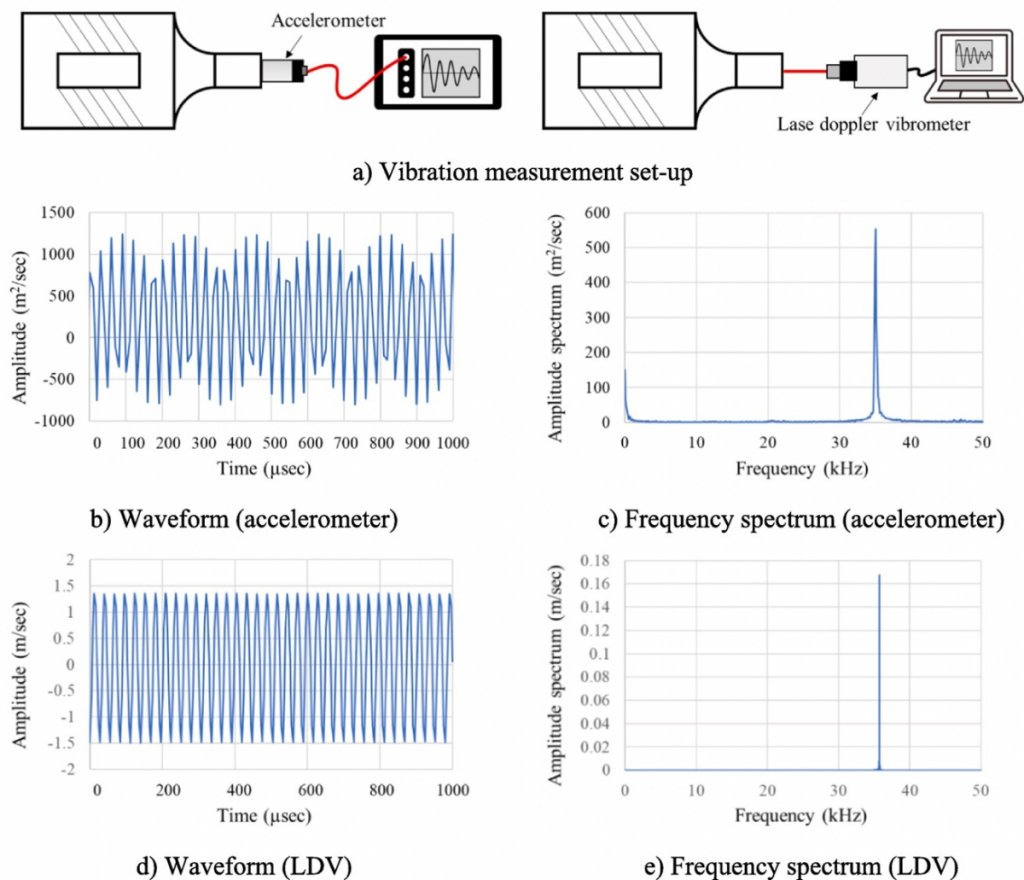
Waveforms for applying very high cycle compressive stress with ultrasonic excitation.
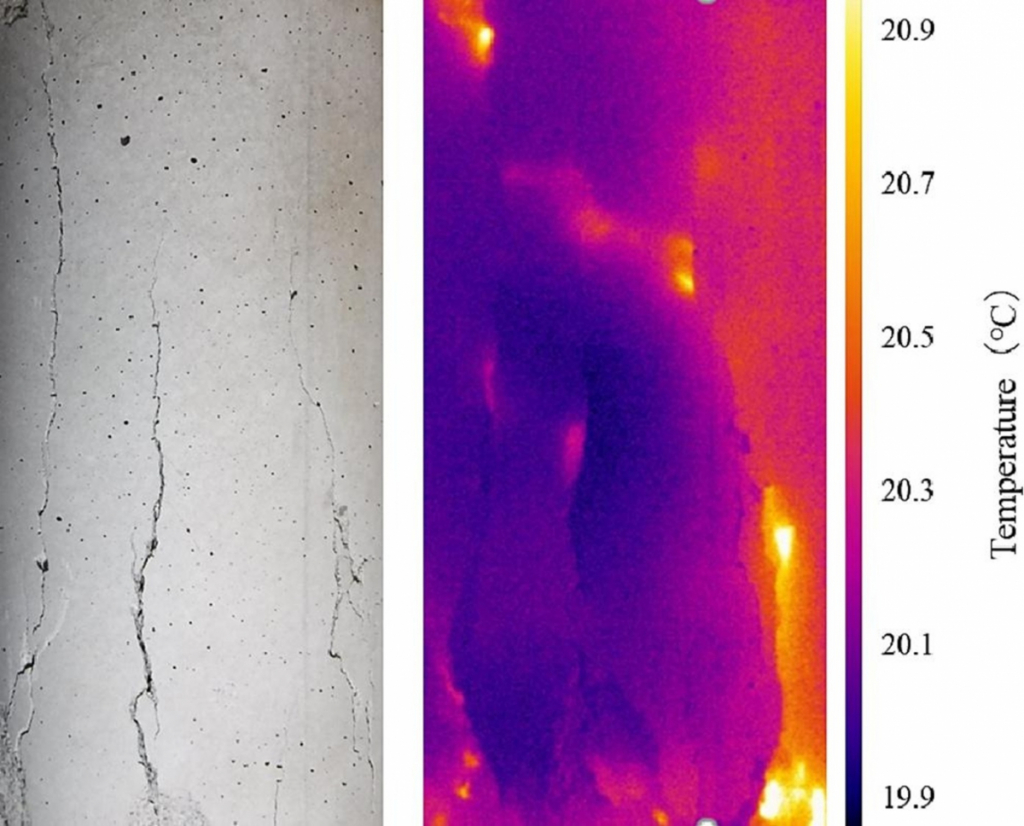
Specimen surface image and Sonic-IR image after compression failure.
研究業績の一例
Katsufumi Hashimoto and Tomoki Shiotani, Sonic-IR imaging technique for detection of crack interfaces in cementitious materials
Construction and Building Materials, Vol.386, 131549, 2023.
その他の研究成果
髙橋尚、橋本勝文、杉山隆文、熊谷駿佑、サーモソニック法によるモルタル内部の損傷度と発熱挙動の評価
コンクリ-ト構造物の補修,補強,アップグレ-ド論文報告集,Vol.23,pp.245-250,2023.
Development of sensing device with MEMS technology for structural and environmental condition in service
インフラモニタリングおよび環境センシングを目的とした革新的MEMS技術によるデバイス開発
海洋環境等に暴露される鉄筋コンクリート(RC)構造物の効率的なモニタリングシステムは,塩化物による鉄筋の腐食によって構造物が劣化するリスクを想定した場合に大変重要です。従来のメンテナンス手法では膨大な予算が必要となっていることからも,先進技術に依存した省コストかつ省人化に資する革新的なアプローチが最重要となります。本研究では、MEMS(Micro Electro Mechanical Systems)をベースとしたマイクロエネルギーハーベスタ(MEH)を技術的に応用し,供用環境中で誘起される振動による静電発電に着目することで,対象構造物の節点位置における固有振動数と振幅の変化を観察することにより構造物のリアルタイムモニタリングを可能にした迅速なセンサネットワークを提供できると考えています。
The need for efficient monitoring systems for reinforced concrete (RC) structures near marine environments is essential, driven by the heightened risk of structural degradation due to chloride-induced corrosion of reinforcing bars. Thus, huge amounts of budgets are consumed by traditional maintenance methodologies. To address this challenge, a proactive and innovative approach relying on advanced technologies becomes paramount. In this study, Micro Energy Harvester (MEH) based on Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) is technically applied to develop a sensor to identify the corrosion environment with chlorides in the exposure condition. MEMS devices offer rapid evolution, enabling real-time monitoring of the structure by observing changes in natural frequency and amplitude at nodal locations of the targeting structure due to vibration-based electrostatic power generation induced by the corrosive environment.
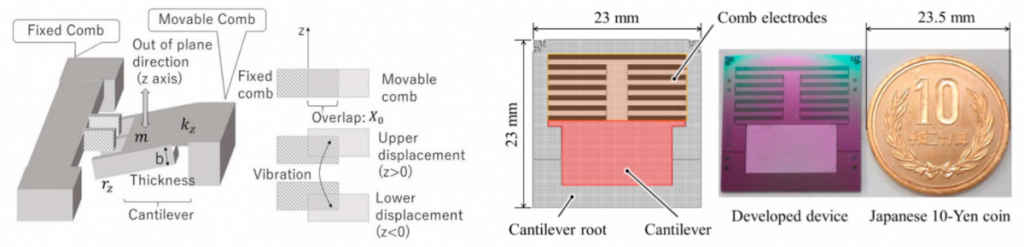
Development of a Cantilever-Type Electrostic Energy Harvester and its Charging Characteristics on a Highway Viaduct
Koga, H., Mitsuya, H., Honma, H., Fujita, H., Toshiyoshi, H., Hashiguchi, G., Micromachines, 8, 293, 2017.
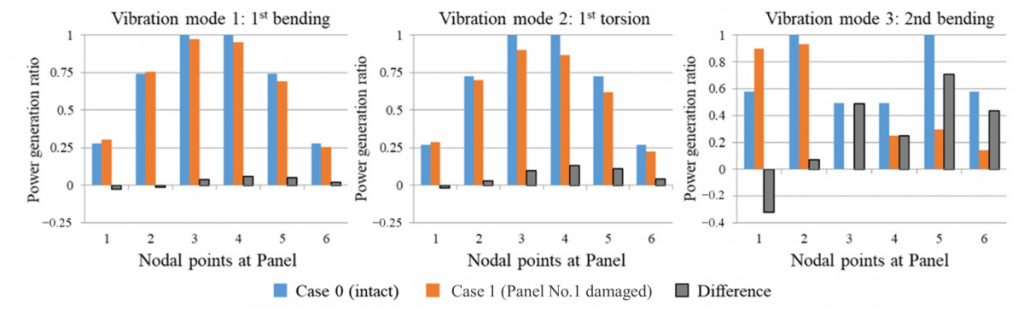
Output power generated by MEH for identification of damage location (RC Slab model with 6 panels).
研究業績の一例
Katsufumi Hashimoto, Tomoki Shiotani, Hiroyuki Mitsuya, Kai Chun Chang, MEMS Vibrational Power Generator for Bridge Slab and Pier Health Monitoring
Applied Sciences, 10 (22), 8198, 2020.
その他の研究成果
Kai-Chun Chang, Katsufumi Hashimoto, Hiroyuki Mitsuya, Tomoki Shiotani, Electrostatic micro-electro-mechanical system vibrational energy harvesters for bridge damage detection
The Rise of Smart Cities, Elsevier Book Chapter Elsevier, pp.319-342, 2022.
Utilization of industrial by-products as cementitious materials and corrosion resistance of reinforced concrete
産業副産物の積極的利用と鉄筋コンクリートの耐久性
フライアッシュや高炉スラグなどの産業副産物は,温室効果ガスの排出などコンクリートの環境負荷を低減し,厳しい気候条件下でのコンクリート構造物の性能を向上させるために,普通ポルトランドセメントの代わりに使用されています。産業副産物を利用したコンクリートの耐久性,強度発現性,ひび割れ抵抗性を本研究の主な対象としています。特に、フライアッシュや高炉スラグを用いたコンクリート中の塩害や凍害による鋼材の耐腐食性については,コンクリート構造物の耐久性向上設計の視座から研究を行っています。
Industrial by-products such as fly ash and blast furnace slag are used in place of ordinary Portland cement in order to reduce the embedded environmental impacts of concrete, such as greenhouse gas emissions, as well as enhance the performance of concrete structures under severe climate conditions. Durability, strength development, and crack resistance of concretes utilizing industrial by-products are the primary targets of this studies. In particular, the corrosion resistance of embedded steel due to salt attack and frost damage in fly ash or slag concretes are studied in order to implement improved durability design for concrete structures.
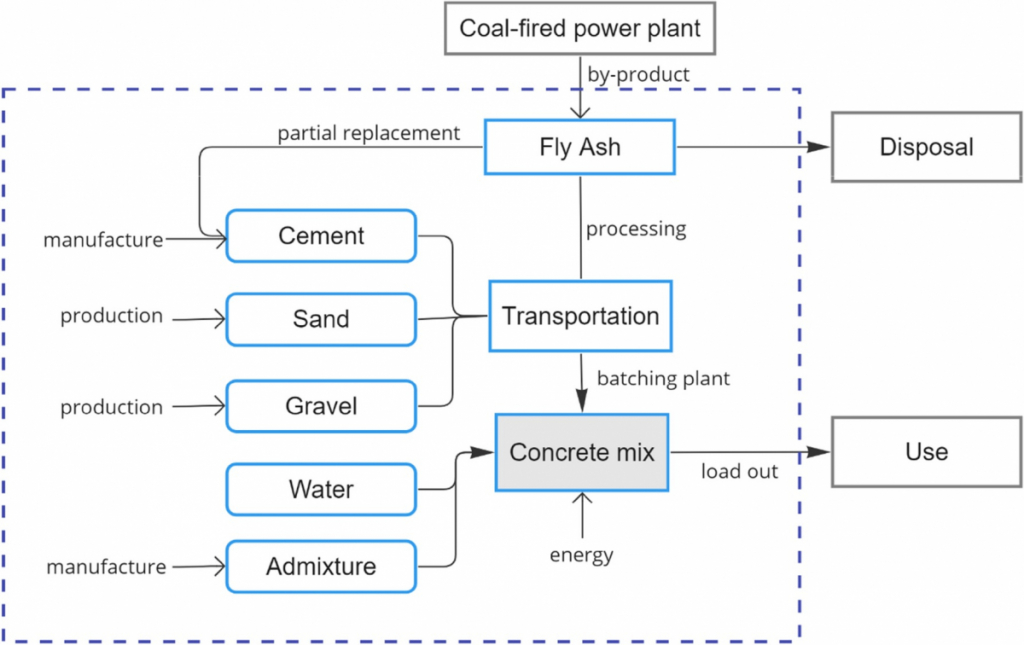
System boundary used in life cycle assessment of mass concrete production.
研究業績の一例
Ni Wang, Takafumi Sugiyama, Corrosion evaluation of steel bars in steam-cured concrete under chloride attack and alkali–silica reaction
Magazine of Concrete Research, 75(9), pp.433-446, 2023.
その他の研究成果
Christian Orozco, Somnuk Tangtermsirikul, Takafumi Sugiyama, Sandhya Babel, Examining the endpoint impacts, challenges, and opportunities of fly ash utilization for sustainable concrete construction
Scientific Reports (Springer Nature), 13(1), 18254, 2023.

